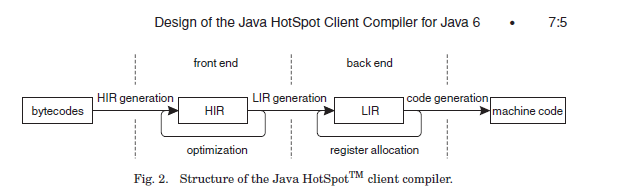
C1コンパイラの内部構造¶
コンパイラ全体の制御¶
c1_Compiler.cpp コンパイルの入り口
// 入力はciMethond* method <-- bytecode method単位
void Compiler::compile_method(ciEnv* env, ciMethod* method, int entry_bci)
compile_method()
c1_Compilation.cpp コンパイラの全体制御
Compilation::compile_method()
method()->break_at_execute()
compile_java_method()
install_code(frame_size)
Compilation::compile_java_method()
build_hir()
_hir = new IR()
_hir->optimize()
_hir->split_critical_edges()
_hir->compute_code()
GlobalValueNumbering gvn(_hir)
_hir->compute_use_counts()
FrameMap()
emit_lir()
LIRGenerator gen()
hir()->iterate_linear_scan_order()
LinearScan allocator = new LinearScan()
allocator->do_linear_scan()
compute_local_live_sets()
compute_global_live_sets()
build_intervals()
allocate_registers()
resolve_data_flow()
propagate_spill_slots()
eliminate_spill_moves()
assign_reg_num()
allocate_fpu_stack()
EdgeMoveOptimizer::optimize(ir()->code())
ControlFlowOptimizer::optimize(ir()->code())
emit_code_body()
setup_code_buffer()
_masm = new C1_MacroAssembler()
LIR_Asssembler lir_asm()
lir_asm.emit_code()
emit_code_epilog()
generate code for deopt handler
BytecodeからHIRへの変換¶
BytecodeからHIRへの変換は、大体1Bytecodeにつき、1HIRに変換する
IR()
IR()->IRScope()->XHandlers()
IRScope()
_requires_phi_function
IR()->IRScope()->IRScope()
_start = GraphBuilder gm() constructor
GraphBuilder()
GraphBuilder::iterate_all_blocks()
GraphBuilder::iterate_bytecodes_for_block(int bci)
Bytecodeの各命令ごとに処理をわけているところ
GraphBuilder::iterate_bytecodes_for_block(int bci):
_skip_block = false;
assert(state() != NULL, "ValueStack missing!");
ciBytecodeStream s(method());
s.reset_to_bci(bci);
int prev_bci = bci;
scope_data()->set_stream(&s);
// iterate
Bytecodes::Code code = Bytecodes::_illegal;
bool push_exception = false;
if (block()->is_set(BlockBegin::exception_entry_flag) && block()->next() == NULL) {
// first thing in the exception entry block should be the exception object.
push_exception = true;
}
while (!bailed_out() && last()->as_BlockEnd() == NULL &&
(code = stream()->next()) != ciBytecodeStream::EOBC() &&
(block_at(s.cur_bci()) == NULL || block_at(s.cur_bci()) == block())) {
assert(state()->kind() == ValueStack::Parsing, "invalid state kind");
// Check for active jsr during OSR compilation
if (compilation()->is_osr_compile()
&& scope()->is_top_scope()
&& parsing_jsr()
&& s.cur_bci() == compilation()->osr_bci()) {
bailout("OSR not supported while a jsr is active");
}
if (push_exception) {
apush(append(new ExceptionObject()));
push_exception = false;
}
// handle bytecode
switch (code) {
case Bytecodes::_nop : /* nothing to do */ break;
case Bytecodes::_aconst_null : apush(append(new Constant(objectNull ))); break;
case Bytecodes::_iconst_m1 : ipush(append(new Constant(new IntConstant (-1)))); break;
case Bytecodes::_iconst_0 : ipush(append(new Constant(intZero ))); break;
case Bytecodes::_iconst_1 : ipush(append(new Constant(intOne ))); break;
case Bytecodes::_iconst_2 : ipush(append(new Constant(new IntConstant ( 2)))); break;
case Bytecodes::_iconst_3 : ipush(append(new Constant(new IntConstant ( 3)))); break;
case Bytecodes::_iconst_4 : ipush(append(new Constant(new IntConstant ( 4)))); break;
case Bytecodes::_iconst_5 : ipush(append(new Constant(new IntConstant ( 5)))); break;
...
case Bytecodes::_invokevirtual : // fall through
case Bytecodes::_invokespecial : // fall through
case Bytecodes::_invokestatic : // fall through
case Bytecodes::_invokedynamic : // fall through
case Bytecodes::_invokeinterface: invoke(code); break;
invoke命令を変換時にdevirtualize/inline展開する
- @todo codeを追う
- @todo devirtualizeの仕組み
- @todo is_profile_callの仕組み
if_icmpXXの変換¶
if_icmpXXの変換が分かりやすい
Bytecodeのiterate
case Bytecodes::_if_icmpeq : if_same(intType , If::eql); break;
case Bytecodes::_if_icmpne : if_same(intType , If::neq); break;
case Bytecodes::_if_icmplt : if_same(intType , If::lss); break;
case Bytecodes::_if_icmpge : if_same(intType , If::geq); break;
case Bytecodes::_if_icmpgt : if_same(intType , If::gtr); break;
case Bytecodes::_if_icmple : if_same(intType , If::leq); break;
case Bytecodes::_if_acmpeq : if_same(objectType, If::eql); break;
case Bytecodes::_if_acmpne : if_same(objectType, If::neq); break;
ifの変換部
void GraphBuilder::if_same(ValueType* type, If::Condition cond) {
ValueStack* state_before = copy_state_before();
Value y = pop(type);
Value x = pop(type);
if_node(x, cond, y, state_before);
}
void GraphBuilder::if_node(Value x, If::Condition cond, Value y, ValueStack* state_before) {
BlockBegin* tsux = block_at(stream()->get_dest());
BlockBegin* fsux = block_at(stream()->next_bci());
bool is_bb = tsux->bci() < stream()->cur_bci() || fsux->bci() < stream()->cur_bci();
Instruction *i = append(new If(x, cond, false, y, tsux, fsux, is_bb ? state_before : NULL, is_bb));
if (is_profiling()) {
If* if_node = i->as_If();
if (if_node != NULL) {
// Note that we'd collect profile data in this method if we wanted it.
compilation()->set_would_profile(true);
// At level 2 we need the proper bci to count backedges
if_node->set_profiled_bci(bci());
if (profile_branches()) {
// Successors can be rotated by the canonicalizer, check for this case.
if_node->set_profiled_method(method());
if_node->set_should_profile(true);
if (if_node->tsux() == fsux) {
if_node->set_swapped(true);
}
}
return;
}
// Check if this If was reduced to Goto.
Goto *goto_node = i->as_Goto();
if (goto_node != NULL) {
compilation()->set_would_profile(true);
if (profile_branches()) {
goto_node->set_profiled_method(method());
goto_node->set_profiled_bci(bci());
goto_node->set_should_profile(true);
// Find out which successor is used.
if (goto_node->default_sux() == tsux) {
goto_node->set_direction(Goto::taken);
} else if (goto_node->default_sux() == fsux) {
goto_node->set_direction(Goto::not_taken);
} else {
ShouldNotReachHere();
}
}
return;
}
}
}
invokeの変換¶
BytecodeのinvokeXXXは、invoke()メソッドで処理する。
invokeを処理する際に、呼び出し対象が一意に定まるか判定し、
もし定まる場合は、inline展開を試行する。
また、invokevirtualやinvokeinterfaceのdevirtual化(invokespecialとみなす)を行い、 積極的にinline展開を試行する
invoke
switch (code) {
case Bytecodes::_nop : /* nothing to do */ break;
...
case Bytecodes::_invokevirtual : // fall through
case Bytecodes::_invokespecial : // fall through
case Bytecodes::_invokestatic : // fall through
case Bytecodes::_invokedynamic : // fall through
case Bytecodes::_invokeinterface: invoke(code); break;
GraphBuilder::invoke(Bytecodes::Code)
ciMethod* cha_monomorphic_target
ciMethod* exact_target
if (!target->is_static()) {
type_is_exact
exact_target = target->resolve_invoke(calling_klass, receiver_klass);
code = invokespecial
invokevirtual || invokeinterfaceの場合
cha_monomorphic_target = target->find_monomorphic_target(calling_klass, callee_holder, actual_recv);
invokeinterface && singleton?
CheckCast* c = new CheckCast(klass, receiver, copy_state_for_exception())
set_incompatible_class_change_check()
cha_monomorphic_targetがabstractだった場合、
NULL
cha_monomorphic_targetが見つかった場合
dependency_recorder()->assert_unique_concrete_method(actual_recv, cha_monomorphic_target)
code = invokespecial
もし上記処理で一意に分かったら
try_inline(inline_target, );
try_inline_full() <-- 200stepの関数なので、あまり見たくない
最終的には、iterate_bytecode_ みたいなのを呼び出す
is_profiling()
target_klass = cha_monomorphic_target->holder() || exact_garget->holder()
profile_call(recv, target_klass)
dependency¶
dependencyは、JVM上での制約をチェックし、違反した場合イベントを起動してくれるイベントハンドラみたいなもの
よく脱仮想化する際に使用し、もし脱仮想化の条件が崩れた場合、脱最適化するようにイベントを登録する
脱仮想化の条件が崩れる例として、newで新しいクラスを作成した時や、classloader、redefine
void GraphBuilder::invoke(Bytecodes::Code code)
if (cha_monomorphic_target != NULL) {
if (!(target->is_final_method())) {
// If we inlined because CHA revealed only a single target method,
// then we are dependent on that target method not getting overridden
// by dynamic class loading. Be sure to test the "static" receiver
// dest_method here, as opposed to the actual receiver, which may
// falsely lead us to believe that the receiver is final or private.
dependency_recorder()->assert_unique_concrete_method(actual_recv, cha_monomorphic_target);
}
code = Bytecodes::_invokespecial;
}
GraphBuilder::call_register_finalizer()
ciInstanceKlass* ik = compilation()->method()->holder();
//finalだったら、一意
if (ik->is_final()) {
exact_type = ik;
//クラス階層解析を使用するかつサブクラスを持ってない
} else if (UseCHA && !(ik->has_subklass() || ik->is_interface())) {
// test class is leaf class
compilation()->dependency_recorder()->assert_leaf_type(ik);
exact_type = ik;
} else {
declared_type = ik;
}
Dependencyを試す場合のオプション
-XX:+TraceDependencies
-XX:+VerifyDependencies
dependencyの制約にひっかかり、deoptimizeするサンプルプログラム
deoptimize sample
interface getter {
public int num();
public int get();
}
class Bgetter implements getter {
public int num() {
return 1;
}
public int get() {
int sum = 0;
for (int i=0; i<100; i++) {
sum += num();
}
return sum;
}
}
class Cgetter implements getter {
public int num() {
return 2;
}
public int get() {
int sum = 0;
for (int i=0; i<100; i++) {
sum += num();
}
return sum;
}
}
public class iftest {
static final long LEN=100000000;
public static void main(String args[]) {
getter f = new B();
long sum=0;
for( long i=0; i<LEN; i++ ) {
sum += f.get();
}
// getter f2 = new C(); //devirtualize
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
getter f2のコメントを外すと、new C()された際にdependencyが反応し、deoptimizeが走る
log
Failed dependency of type unique_concrete_method
context = *getter
method = {method} 'get' '()I' in 'B'
witness = *getter
code: 9434 1% nmethod iftest::main @ 13 (58 bytes)
Marked for deoptimization
context = getter
dependee = C
context supers = 1, interfaces = 1
Compiled (c1) 9434 1% nmethod iftest::main @ 13 (58 bytes)
total in heap [0xb5891388,0xb5891acc] = 1860
relocation [0xb5891458,0xb5891500] = 168
main code [0xb5891500,0xb58917c0] = 704
stub code [0xb58917c0,0xb589180c] = 76
oops [0xb589180c,0xb5891818] = 12
scopes data [0xb5891818,0xb58918ec] = 212
scopes pcs [0xb58918ec,0xb5891aac] = 448
dependencies [0xb5891aac,0xb5891ab0] = 4
nul chk table [0xb5891ab0,0xb5891acc] = 28
Dependencies:
Dependency of type unique_concrete_method
context = *getter
method = {method} 'get' '()I' in 'B'
[nmethod<=klass]getter
checking (true) 9434 1% nmethod iftest::main @ 13 (58 bytes)
depdnecyのcheck処理が呼ばれた際のstack trace
Breakpoint 4, Dependencies::DepStream::check_dependency_impl (this=0xfd05c8, changes=0xfd06f8)
at /home/elise/language/openjdk6/hotspot/src/share/vm/code/dependencies.cpp:1449
1449 if (TraceDependencies) {
#1 0x00530b7e in Dependencies::DepStream::spot_check_dependency_at (this=0xfd05c8, changes=...)
at /home/elise/language/openjdk6/hotspot/src/share/vm/code/dependencies.cpp:1464
1464 return check_dependency_impl(&changes);
#0 Dependencies::DepStream::check_dependency_impl (this=0xfd05c8, changes=0xfd06f8)
at /home/elise/language/openjdk6/hotspot/src/share/vm/code/dependencies.cpp:1449
1449 if (TraceDependencies) {
#1 0x00530b7e in Dependencies::DepStream::spot_check_dependency_at (this=0xfd05c8, changes=...)
at /home/elise/language/openjdk6/hotspot/src/share/vm/code/dependencies.cpp:1464
1464 return check_dependency_impl(&changes);
#2 0x007573ae in nmethod::check_dependency_on (this=0xb60d4388, changes=...)
at /home/elise/language/openjdk6/hotspot/src/share/vm/code/nmethod.cpp:2063
2063 if (deps.spot_check_dependency_at(changes) != NULL) {
#3 0x005b6030 in instanceKlass::mark_dependent_nmethods (this=0xb212bde0, changes=...)
at /home/elise/language/openjdk6/hotspot/src/share/vm/oops/instanceKlass.cpp:1406
1406 if (nm->is_alive() && !nm->is_marked_for_deoptimization() && nm->check_dependency_on(changes)) {
#4 0x004b0f83 in CodeCache::mark_for_deoptimization (changes=...)
at /home/elise/language/openjdk6/hotspot/src/share/vm/code/codeCache.cpp:641
641 number_of_marked_CodeBlobs += instanceKlass::cast(d)->mark_dependent_nmethods(changes);
#5 0x00866302 in Universe::flush_dependents_on (dependee=...)
at /home/elise/language/openjdk6/hotspot/src/share/vm/memory/universe.cpp:1182
1182 if (CodeCache::mark_for_deoptimization(changes) > 0) {
#6 0x00825729 in SystemDictionary::add_to_hierarchy (k=..., __the_thread__=0x806cc00)
at /home/elise/language/openjdk6/hotspot/src/share/vm/classfile/systemDictionary.cpp:1727
1727 Universe::flush_dependents_on(k);
#7 0x00824e09 in SystemDictionary::define_instance_class (k=..., __the_thread__=0x806cc00)
at /home/elise/language/openjdk6/hotspot/src/share/vm/classfile/systemDictionary.cpp:1506
1506 add_to_hierarchy(k, CHECK); // No exception, but can block
#8 0x00823df1 in SystemDictionary::resolve_from_stream (class_name=..., class_loader=..., protection_domain=..., st=0xfd0980,
verify=true, __the_thread__=0x806cc00) at /home/elise/language/openjdk6/hotspot/src/share/vm/classfile/systemDictionary.cpp:1138
1138 define_instance_class(k, THREAD);
#9 0x0064c2d9 in jvm_define_class_common (env=0x806cd3c, name=0xfd0eac "C", loader=0xfd0fac, buf=0xa1c16508 "\312\376\272\276",
len=316, pd=0xfd0f98, source=0xfd0aac "file:/home/elise/language/java/sample6/", verify=1 '\001', __the_thread__=0x806cc00)
at /home/elise/language/openjdk6/hotspot/src/share/vm/prims/jvm.cpp:864
864 CHECK_NULL);
#10 0x0064c7d6 in JVM_DefineClassWithSource (env=0x806cd3c, name=0xfd0eac "C", loader=0xfd0fac, buf=0xa1c16508 "\312\376\272\276",
len=316, pd=0xfd0f98, source=0xfd0aac "file:/home/elise/language/java/sample6/")
at /home/elise/language/openjdk6/hotspot/src/share/vm/prims/jvm.cpp:884
884 return jvm_define_class_common(env, name, loader, buf, len, pd, source, true, THREAD);
#11 0x00ff7942 in Java_java_lang_ClassLoader_defineClass1 (env=0x806cd3c, loader=0xfd0fac, name=0xfd0fa8, data=0xfd0fa4, offset=0,
length=316, pd=0xfd0f98, source=0xfd0f94) at ../../../src/share/native/java/lang/ClassLoader.c:151
151 result = JVM_DefineClassWithSource(env, utfName, loader, body, length, pd, utfSource);
@todo DepStream::check_dependency_impl() code/dependencies.cpp
invokenの際は、unique_concreate_method
CHAで再度チェックしている
klassOop Dependencies::DepStream::check_dependency_impl(DepChange* changes) {
assert_locked_or_safepoint(Compile_lock);
klassOop witness = NULL;
switch (type()) {
case evol_method:
witness = check_evol_method(method_argument(0));
break;
case leaf_type:
witness = check_leaf_type(context_type());
break;
case abstract_with_unique_concrete_subtype:
witness = check_abstract_with_unique_concrete_subtype(context_type(),
type_argument(1),
changes);
break;
case abstract_with_no_concrete_subtype:
witness = check_abstract_with_no_concrete_subtype(context_type(),
changes);
break;
case concrete_with_no_concrete_subtype:
witness = check_concrete_with_no_concrete_subtype(context_type(),
changes);
break;
case unique_concrete_method:
witness = check_unique_concrete_method(context_type(),
method_argument(1),
changes);
break;
case abstract_with_exclusive_concrete_subtypes_2:
witness = check_abstract_with_exclusive_concrete_subtypes(context_type(),
type_argument(1),
type_argument(2),
changes);
break;
case exclusive_concrete_methods_2:
witness = check_exclusive_concrete_methods(context_type(),
method_argument(1),
method_argument(2),
changes);
break;
case no_finalizable_subclasses:
witness = check_has_no_finalizable_subclasses(context_type(),
changes);
break;
default:
witness = NULL;
ShouldNotReachHere();
break;
}
deoptimizeも、thread並列で行うが、実際にコードを置換する際には全体をmutexで止める
dependenceからDeoptimizeを呼び出す場所
// Flushes compiled methods dependent on dependee.
void Universe::flush_dependents_on(instanceKlassHandle dependee) {
assert_lock_strong(Compile_lock);
if (CodeCache::number_of_nmethods_with_dependencies() == 0) return;
// CodeCache can only be updated by a thread_in_VM and they will all be
// stopped dring the safepoint so CodeCache will be safe to update without
// holding the CodeCache_lock.
DepChange changes(dependee);
// Compute the dependent nmethods
if (CodeCache::mark_for_deoptimization(changes) > 0) { //<----- koko
// At least one nmethod has been marked for deoptimization
VM_Deoptimize op;
VMThread::execute(&op);
}
}
dependenciesのルールから、VM_deoptimizeがキックされ、 dependenciesに引っかかった要素をdeoptimizeする
deoptimizeも、2種類あり、mutexで止めた際に、実行中でないなら、oopsのcodeを書き換える抱け。
もし実行中だったら、frameを書き換えて、JITコンパイルしたコードからintepreter実行に切り替える
プロファイラ¶
C1コンパイラでは、
プロファイルした情報を活用する部分と、
C1コンパイラが生成したコードにプロファイルする命令を埋め込む部分がある。
プロファイル系のオプション
product(bool, C1ProfileCalls, true, \
"Profile calls when generating code for updating MDOs") \
\
// dead
product(bool, C1ProfileVirtualCalls, true, \
"Profile virtual calls when generating code for updating MDOs") \
\
product(bool, C1ProfileInlinedCalls, true, \
"Profile inlined calls when generating code for updating MDOs") \
\
product(bool, C1ProfileBranches, true, \
"Profile branches when generating code for updating MDOs") \
\
product(bool, C1ProfileCheckcasts, true, \
"Profile checkcasts when generating code for updating MDOs") \
主にプロファイルはインタプリタが行っているが、
C1コンパイラがJITコンパイルしたコードにも埋め込み可能になっている。
JITコンパイルしたコードに埋め込む場合、2回目、3回目のJITコンパイルが行われるはず
複数回のJITコンパイルの条件は不明。。
プロファイルの様子は、TemplateIntepreterの解説に期待
HIR から LIR への変換¶
HIRからLIRへの変換はLIRGeneratorが行う。
visitorでHIRを走査し、HIRに対して複数のLIRへ分解する
LIRは仮想レジスタを無限に持つことを仮定し、レジスタ割り付けで実レジスタを割り振る
void LIRGenerator::block_do(BlockBegin* block)
block_do_prolog(block);
__ branch_destination(block->label()); <-- label設定
set_block(block);
for (Instruction* instr = block; instr != NULL; instr = instr->next()) {
if (instr->is_pinned()) do_root(instr);
}
set_block(NULL);
block_do_epilog(block);
void LIRGenerator::do_IfOp(IfOp* x)
// Code for : x->x() {x->cond()} x->y() ? x->tval() : x->fval()
LIRItem left(x->x(), this);
LIRItem right(x->y(), this);
left.load_item();
if (can_inline_as_constant(right.value())) {
right.dont_load_item();
} else {
right.load_item();
}
LIRItem t_val(x->tval(), this);
LIRItem f_val(x->fval(), this);
t_val.dont_load_item();
f_val.dont_load_item();
LIR_Opr reg = rlock_result(x);
__ cmp(lir_cond(x->cond()), left.result(), right.result());
__ cmove(lir_cond(x->cond()), t_val.result(), f_val.result(), reg, as_BasicType(x->x()->type()));
}
invokeの処理なんかは複雑で面白いかもしれない